One of the best ways to increase your online privacy and security is to use a VPN service. What do they do? They give you access to content in other countries, stop your ISP and employer from logging your browsing history, and foil advertisers who want to track the products you’re most interested in.
But all of that comes at a cost: it’s likely you won’t achieve the same internet speed as you would usually. If you’re using a VPN, I imagine you’ve already noticed that.

How much slower that is depends on several factors. These include the VPN provider you’ve chosen, the server you’ve connected to, how many people are using the service at the same time, and the settings you have chosen.
In this article, we’ll explain each cause and how to minimize its effect.
Table of Contents
1. Maybe Your VPN Isn’t the Problem
If your internet seems slow, first check to see if the trouble is actually coming from your VPN. It may be that your internet connection or computer is running slow. Start by performing speed tests when disconnected and connected to your VPN.
If your connection is slow even when you’re not connected to the VPN, run through some common troubleshooting steps:
- Restart your router
- Restart your computer or device
- Switch to a wired ethernet connection
- Temporarily disable your antivirus software and firewall
2. VPNs Encrypt Your Data
A VPN protects your privacy by encrypting your traffic from the time it leaves your computer. That means that your ISP, employer, government, and others won’t be able to tell which websites you visit. However, encrypting your data takes time—and that will slow your connection.
In general, the more secure the encryption, the longer it will take. Some VPN services allow you to select which protocol is used. You can choose whether to prioritize security or speed.
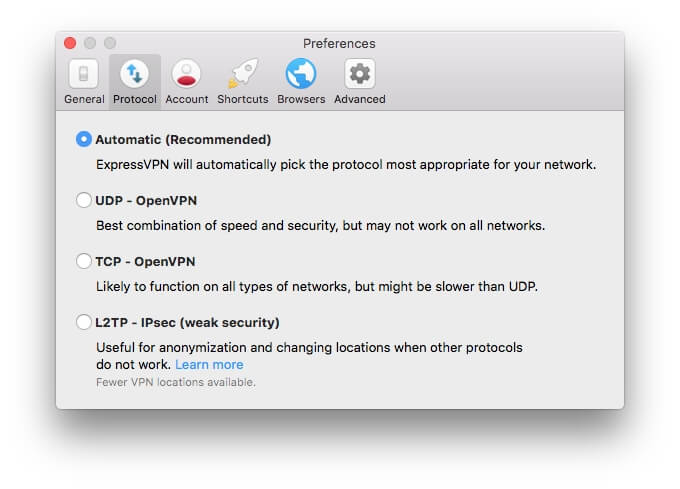
This screenshot shows the available protocols for ExpressVPN. OpenVPN is the most commonly used protocol; either the UDP or TCP may be faster on your computer, so it’s worth trying both. But you may get even faster speeds with the alternatives.
Not all protocols offer the level of security as OpenVPN, and as a result, they may be faster. Tech Times summarizes the difference between security protocols:
- PPTP is the fastest protocol, but its security is very outdated and should only be used when security is not a concern
- L2TP / IPSec is slow and uses a decent security standard
- OpenVPN offers above-average security and acceptable speed, making it suitable for everyday use
- SSTP is faster than the other protocols listed except for PPTP
SSTP seems to be the best option to try. The Surfshark blog recommends another protocol, IKEv2, which offers fairly high security and a fast connection.
There’s a promising new protocol called WireGuard. Some found that it doubled their speed compared to OpenVPN. It’s not yet available on all VPN services.
NordVPN offers the most complete support and labels the protocol “NordLynx.”
3. You Connect to a Remote VPN Server
Your IP address uniquely identifies you online. It allows you to connect with websites—but it also lets others know your approximate location and ties your browsing history to your identity.
A VPN solves this privacy problem by routing all traffic through a VPN server. Now the websites that you connect to see the server’s IP address, not your own. It appears that you are located where the server is, and your browsing history won’t be tied to your identity. But accessing a website via a server is not as fast as accessing it directly.
A VPN allows you to connect to servers worldwide. In general, the further away the server is, the slower your connection will become.
The Surfshark blog also explains why this happens:
- Packet loss: your data is transmitted via packets, which are more likely to get lost when traveling over longer distances.
- More networks to pass through: your data will have to pass through several networks before getting to the server, slowing your connection.
- International bandwidth limitations: Some countries have bandwidth limits. They slow your connection when you send too much data.
How much slower will you be when connected to a distant server? That varies from VPN to VPN, but here are some download speed examples from two different services. Note that I’m located in Australia and have a 100 Mbps connection.
NordVPN:
- Disconnected from the VPN: 88.04 Mbps
- Australia (Brisbane): 68.18 Mbps
- US (New York): 22.20 Mbps
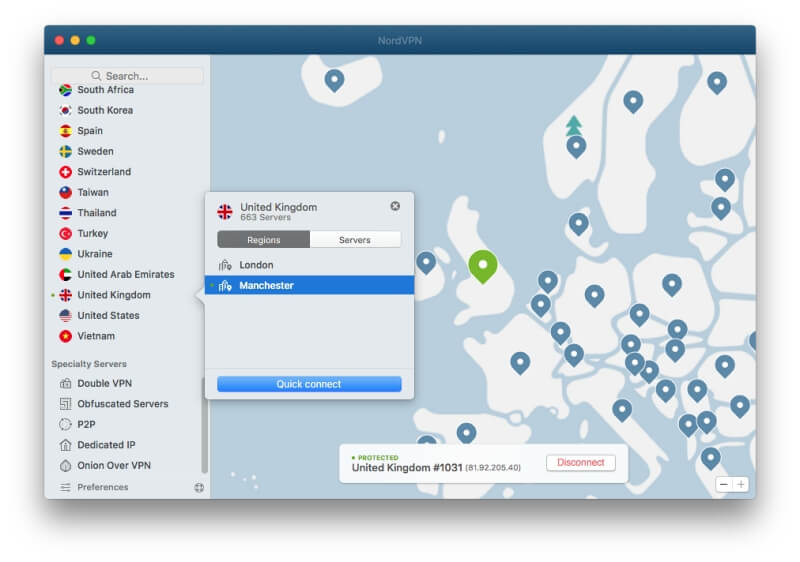
- UK (London): 27.30 Mbps
Surfshark:
- Disconnected from the VPN: 93.73 Mbps
- Australia (Sydney): 62.13 Mbps
- US (San Francisco): 17.37 Mbps
- UK (Manchester): 15.68 Mbps
In each case, the fastest server was close to me, while servers on the other side of the globe were significantly slower. Some VPN services manage much faster international connections.
So, in general, always choose a server that is close to you. Some VPN servers (like Surfshark) will automatically select the fastest server for you.
In short, only consider using a server located somewhere else in the world when you absolutely need to, for example, access content that isn’t available in your own country.
4. Many Users May Be Using the Same VPN Server
If a large number of people connect to the same VPN server simultaneously, it won’t be able to offer its usual bandwidth. Connecting to a different server that is close to you may help.
A VPN with a broad selection of servers may offer fast connections more consistently. Here are the server statistics for many popular VPNs:
- NordVPN: 5100+ servers in 60 countries
- CyberGhost: 3,700 servers in 60+ countries
- ExpressVPN: 3,000+ servers in 94 countries
- PureVPN: 2,000+ servers in 140+ countries
- Surfshark: 1,700 servers in 63+ countries
- HideMyAss: 830 servers in 280 locations across the globe
- Astrill VPN: 115 cities in 64 countries
- Avast SecureLine VPN: 55 locations in 34 countries
- Speedify: servers in 50+ locations around the world
5. Some VPN Services Are Faster Than Others
Finally, some VPN services are simply faster than others. They invest more money in their infrastructure—the quality and number of servers they offer. However, the speeds you achieve with each service may vary depending on where you live in the world.
I performed speed tests on a large number of VPN services. Here are the speeds I recorded from Australia:
- Speedify (two connections): 95.31 Mbps (fastest server), 52.33 Mbps (average)
- Speedify (one connection): 89.09 Mbps (fastest server), 47.60 Mbps (average)
- HMA VPN: 85.57 Mbps (fastest server), 60.95 Mbps (average)
- Astrill VPN: 82.51 Mbps (fastest server), 46.22 Mbps (average)
- NordVPN: 70.22 Mbps (fastest server), 22.75 Mbps (average)
- Surfshark: 62.13 Mbps (fastest server), 25.16 Mbps (average)
- Avast SecureLine VPN: 62.04 Mbps (fastest server), 29.85 (average)
- CyberGhost: 43.59 Mbps (fastest server), 36.03 Mbps (average)
- ExpressVPN: 42.85 Mbps (fastest server), 24.39 Mbps (average)
- PureVPN: 34.75 Mbps (fastest server), 16.25 Mbps (average)
The fastest server was typically the closest one; that speed gives you an indication of which services will enable you to achieve the best possible connection. These include Speedify, HMA VPN, and Astrill VPN.
I’ve also listed the average speed I encountered. For each service, I performed speed tests on servers around the world, and that figure is the average of all of them. It indicates which provider will be fastest if you intend to connect to international servers rather than the closest. These happen to be the same providers in a different order: HMA VPN, Speedify, and Astrill VPN.
Speedify is the fastest VPN I’m aware of because it’s able to combine the bandwidth of multiple internet connections—say, your Wi-Fi and a tethered iPhone. I found an improvement of around 5 Mbps when combining connections. The service was also the fastest when using a single connection. However, I don’t believe it’s the best service for many users. In my tests, I was unable to successfully watch Netflix content when connected.
Fast services that can reliably stream Netflix include HMA VPN, Astrill VPN, NordVPN, and Surfshark. If you’re considering switching to a new VPN service to improve your speed, they should be at the top of your list.
So What Should You Do?
Your internet will normally be slower when using a VPN, but that’s a worthwhile tradeoff for improved privacy and security when online. If your speed becomes slow enough to bother you, here’s a brief summary of what you can do:
- Make sure the VPN is the problem
- Connect to a different server—one that is close to you
- Use a faster encryption protocol, such as SSTP, IKEv2 or WireGuard
- Consider a faster VPN service
Alternatively, contact your VPN provider’s technical support team and discuss the issue with them.
