There are many factors that can impact your internet speed. Some of those issues can temporarily manifest on your local computer, on your switch or router, or even with your ISP.
I’m Aaron, a technologist and attorney with almost two decades of experience working with and around technology. I’m sharing my experience in the hopes that you can quickly and effectively fix your troublesome technology issues.
In this article, I’ll walk through my troubleshooting methodology and some of the common causes of internet speed issues.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Some internet issues may not be local or addressable by you.
- You should always troubleshoot slow internet causes before taking additional steps; it’s quick and easy and can save you frustration.
- If you have an internet connection issue, switch connections.
- Alternatively, you can restart your computer and router to try to resolve internet speed issues.
How to Troubleshoot
I want you to take a look at this picture, which is a diagram of a typical modern home network topology.
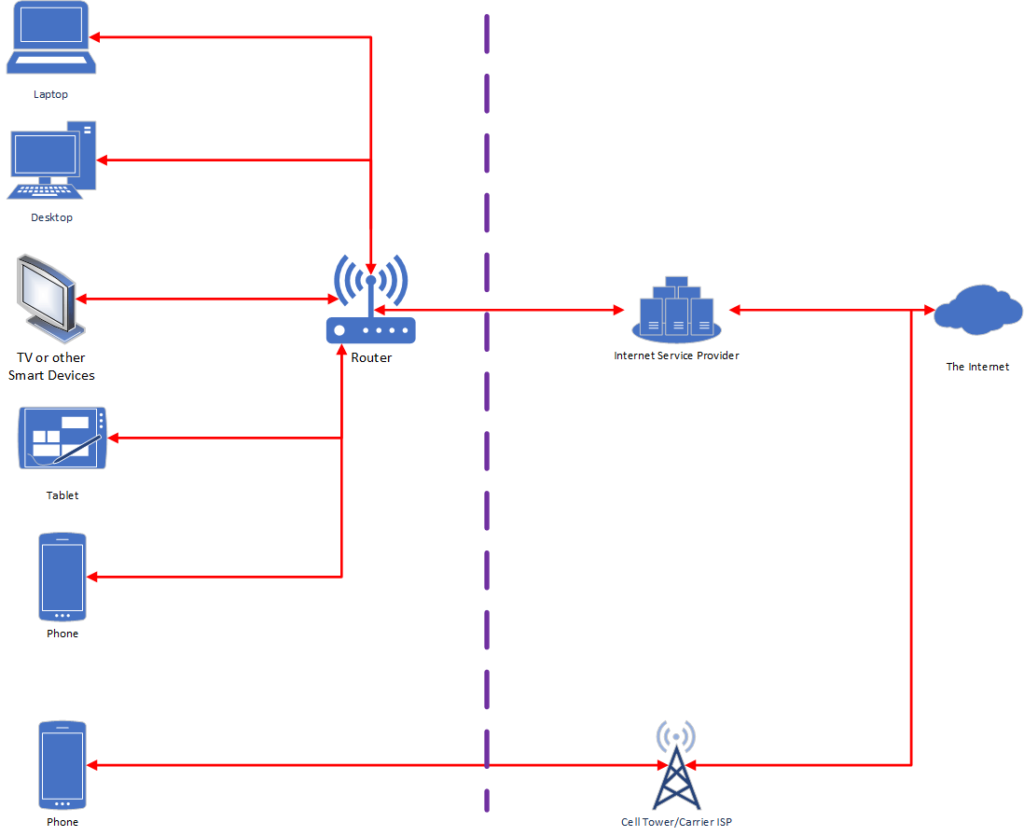
What you’ll see is many common devices connected to a router (typically via Wi-Fi or ethernet cable) which then transmits data to and from an internet service provider, or ISP. The ISP then transmits information to and from other servers, which host the websites and content you consume on the internet.
I also included a smartphone on a cellular connection. Sometimes your devices won’t be connected to your home network and that’s an important distinction to make too.
The diagram and architecture is a significant oversimplification. It’s a helpful one for general troubleshooting. Understand that there’s only so much you can do to troubleshoot and that you’ll only be able to figure out performance issues with what you can touch.
I drew a purple dotted line to demarcate what you can and can’t fix. Everything to the left of that line, you can. Everything to the right of that line, you likely cannot.
You’ll want to take a few steps to troubleshoot. I’ve outlined them in the order I’d recommend you take them in. First…
Figure Out If It’s the Website
If one website loads slowly, visit another. Does that also load slowly? If not, then it might just be the website you’re trying to visit. There’s nothing you can do about that until the website owner fixes the problem.
If both websites load slowly, you’ll also want to run a network speed test. The two major speed tests are speedtest.net and fast.com.
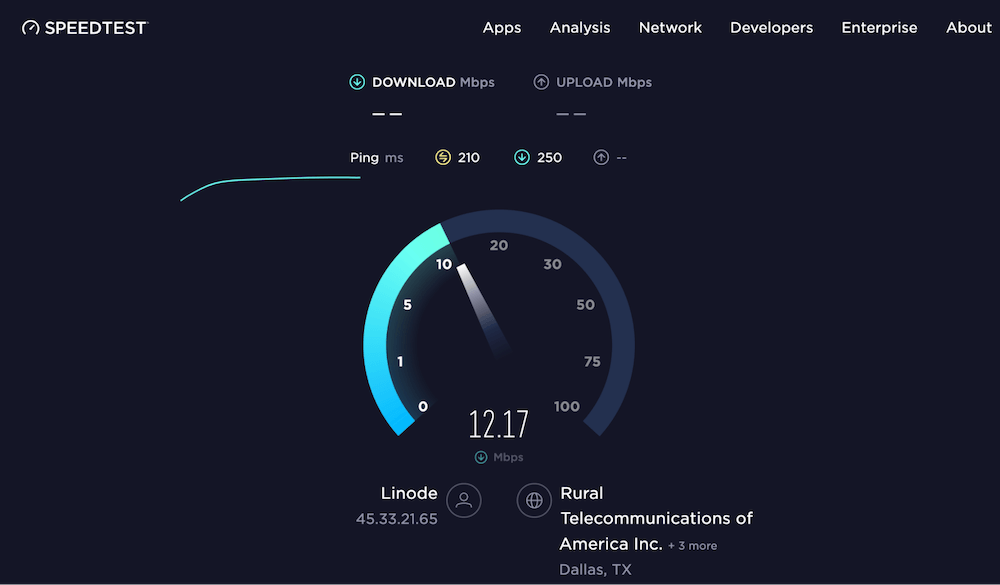
You’ll quickly be able to discern if it’s a website problem. Alternatively and more technically, it could also be a domain resolution problem like when Cloudflare took out large swaths of the internet in June 2022.
If you’re really interested in a deep dive into how that happened, this YouTube video does a great job explaining in detail.
At this point, you can rule out one set of problems with one computer. If you reach anticipated speeds, then it’s the website and not your computer, network, or ISP. You just need to wait it out.
If the speed test also runs slowly, then it’s likely a device, network, or ISP issue and you need to…
Figure Out If It’s the Device or Network
If one device is running slow, but another is not, identify the devices. Are they two computers on the same network? Is one device on an internet connection network and the other connecting via cellular connection?
If you try to visit a website with two computers on the same network (i.e.: the same router connection via wifi or ethernet cable) and one is slow while the other is not, it’s likely a computer or router issue.
If you try to visit a website with a computer or device on an internet connection and another device on a cellular connection and one is slow while the other is not, then it might also be a connectivity issue.
How to Fix the Problem
You’ll want to take a few steps to fix the problem. I’m going to recommend some of the most straightforward solutions that are not very technical and will fix about 99% of your problems.
If your troubleshooting shows that either your internet connection or a cellular network is performing better, then you can…
1. Pick the Better Network
If the internet connection is faster and there’s a Wi-Fi connection, turn on Wi-Fi for all your devices and connect to that network.
If the cellular connection is faster, turn off Wi-Fi for your cellular device. Turn on your Mobile Hotspot, assuming your smart device and wireless plan support it. Follow the instructions to create a local Wi-Fi connection. Connect your non-cellular devices to that Wi-Fi connection.
If you don’t have Mobile Hotspot capabilities, then just use your cellular connected device to browse the internet.
During your troubleshooting, you may have determined it wasn’t the connection at all, but could have been your router or computer. If that’s the case…
2. Restart Your Router and Computer
Have you ever woken up from a full-night’s sleep feeling refreshed and recharged, ready to tackle the day? That’s what restarting your computer does. It dumps temporary processes, flushes the computer memory and temporary files, and lets services and applications update and restart.
While you may be aware that your computer is a computer, you may not be aware that your router is also a computer.
Unplug your router from the power socket. Walk to your computer and restart it. Walk back to your router and plug it back into the power socket. Let both boot. Now check to see if the problem is resolved.
That combination, which is probably going to take a couple minutes at the long end if there are updates to be applied, did a number of things. As described above, it let both devices clear temporary processes. It also reset the network adapters of both devices. If that caused connectivity issues, then they may be resolved. If that didn’t work…
3. Think About Changes You Made
Did you install software recently? Did you make network adapter changes? In both cases, your actions or software could have modified network behavior and can negatively impact speed. Evaluate whether or not you can reset the adapter settings or if you need assistance with that.
My PC Is Not Getting Full Internet Speed
You may have noticed that your computer doesn’t get full advertised speeds. You may run a network speed test and instead of the Gigabit internet you bought, you’re only getting, say, 500 megabits per second (MBPS) or half a Gigabit. How’s that fair?
Your ISP likely has a litany of disclaimers included in your internet services agreement that highlight all the times you won’t get the speed you pay for.
Frankly, they should call internet speed plans theoretical maxima under ideal conditions–which rarely, if ever, exist in real life. You should expect to get anywhere between 50% and 75% of the stated speed of your internet plan.
Also note that internet plan speeds typically only apply to download speeds. That’s important for websites you visit and files you want to download. They rarely apply to upload speeds, which may be orders of magnitude slower.
Your ISP also typically provides no information about your latency, or the time it takes for your message to reach one of the ISPs servers. If you live geographically distant from one of those sites (say, in a rural area) then chances are your latency will be high.
That will impact your perceived internet browsing speed materially. Higher latency means more time to request and load content.
Conclusion
It can be frustrating when your computer doesn’t work as well as it used to. There are a few things you can do to diagnose and address problems. Walking through those steps should address most issues you have. If they don’t then you may need to seek further help.
Do you have any tips for diagnosing network issues? Let me know in the comments below!
